| ||||||||||||||||||
| Ground Penetrating radar | ||||||||||||||||||
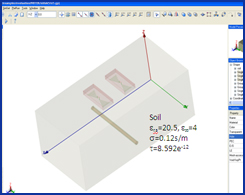
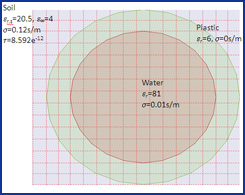
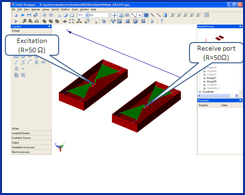
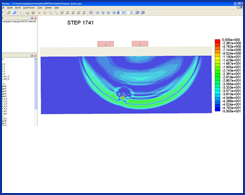
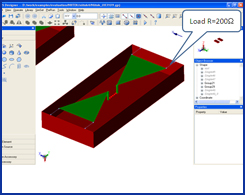
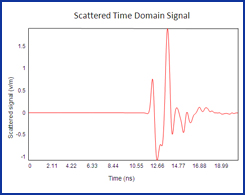
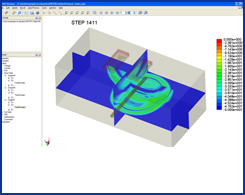
| GEMS is used to simulate a GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) model. A pair of broadband bow-tie antennas are used as the transmitting and receiving antennas. The soil is dispersive medium and the filled water inside the plastic pipe is the lossy material. GEMS is used to extract the time domain scattered signal reflected by the buried pipe. | ||||||||||||||||||
| The basic design procedure in the simulation: | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| The basic settings in the simulation: | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
|